课题组梁莉同学于《Environmental Research》期刊上发表论文,题为《The removal of antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes by sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron activating periodate: Efficacy and mechanism》。
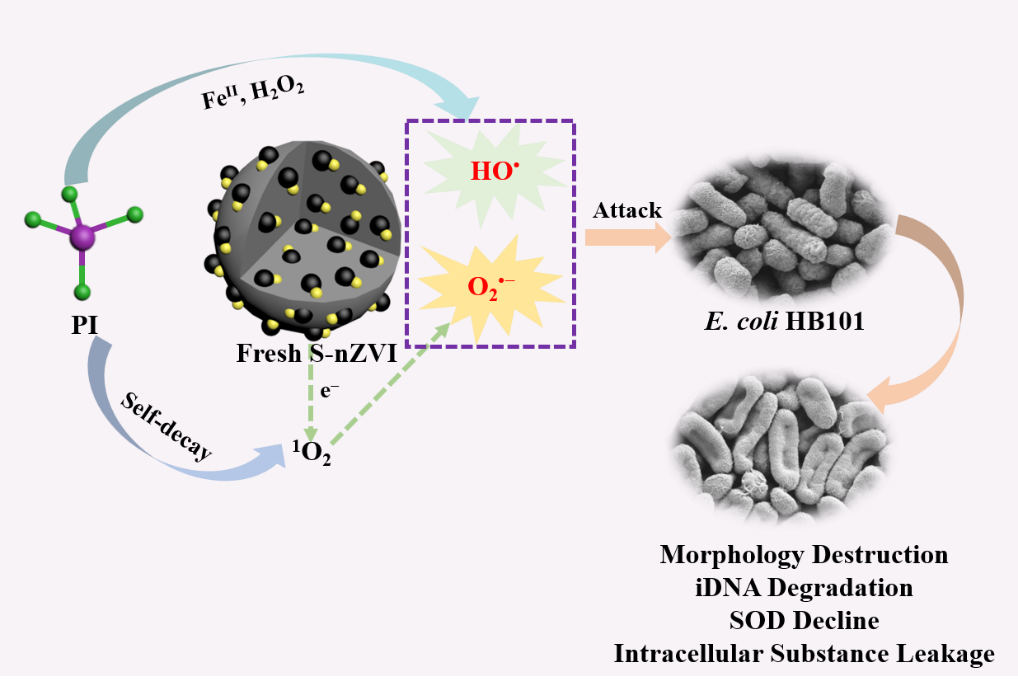
抗生素耐药菌(ARB)和抗生素耐药基因(ARGs)因其对人类健康和生态系统的高风险而受到越来越多的关注。本研究系统研究了硫化纳米级零价铁(S-nZVI)/高碘酸盐(PI)体系对ARB灭活和去除ARGs的性能。S-nZVI/PI系统可在40 min内实现1 × 108 CFU/mL的卡那霉素、氨苄西林和四环素耐药大肠杆菌HB101的完全失活,同时具有清除大肠杆菌HB101携带的胞内ARGs(iARGs)(包括aphA、tetA和tnpA)的能力。反应40 min后,S-nZVI/PI体系对aphA、tetA和tnpA的去除率分别为0.31、0.47和0.39 log10copies/mL。导致大肠杆菌HB101失活的活性物质为HO•和O2•−,可导致大肠杆菌HB101形态和酶系统(如超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化氢酶)的破坏、细胞内物质的损失及iARGs的损伤。此外,还研究了PI和S-nZVI的投加量、大肠杆菌HB101的初始浓度以及共存物质(如HCO3–、NO3–和腐植酸(HA))对大肠杆菌HB101的失活及相应iARGs去除的影响。结果表明,高剂量的PI和S-nZVI以及低浓度的大肠杆菌HB101可以提高S-nZVI/PI系统的灭菌性能。S-nZVI/PI体系中HCO3–、NO3–和HA的存在对大肠杆菌HB101的失活和iARGs的去除具有抑制作用。总的来说,本研究证明了S-nZVI/PI系统在ARB失活和ARGs去除方面的优势。
Abstract: Antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB) and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) have drawn much more attention due to their high risk on human health and ecosystem. In this study, the performance of sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-nZVI)/periodate (PI) system toward ARB inactivation and ARGs removal was systematically investigated. The S-nZVI/PI system could realize the complete inactivation of 1 × 108 CFU/mL kanamycin, ampicillin, and tetracycline-resistant E. coli HB101 within 40 min, meanwhile, possessed the ability to remove the intracellular ARGs (iARGs) (including aphA, tetA, and tnpA) carried by E. coli HB101. Specifically, the removal of aphA, tetA, and tnpA by S-nZVI/PI system after 40 min reaction was 0.31, 0.47, and 0.39 log10copies/mL, respectively. The reactive species attributed to the E. coli HB101 inactivation were HO• and O2•−, which could cause the destruction of E. coli HB101 morphology and enzyme system (such as superoxide dismutase and catalase), the loss of intracellular substances, and the damage of iARGs. Moreover, the influence of the dosage of PI and S-nZVI, the initial concentration of E. coli HB101, as well as the co-existing substance (such as HCO3–, NO3–, and humic acid (HA)) on the inactivation of E. coli HB101 and its corresponding iARGs removal was also conducted. It was found that the high dosage of PI and S-nZVI and the low concentration of E. coli HB101 could enhance the disinfection performance of S-nZVI/PI system. The presence of HCO3–, NO3–, and HA in S-nZVI/PI system showed inhibiting role on the inactivation of E. coli HB101 and its corresponding iARGs removal. Overall, this study demonstrates the superiority of S-nZVI/PI system toward ARB inactivation and ARGs removal.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistant bacteria, Antibiotic resistance genes, Sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron, Periodate, Inactivation
【文章链接入口】