课题组陈继平同学于 《Science of the Total Environment》期刊上发表了题为《Effect of disinfectant exposure and starvation treatment on the detachment of simulated drinking water biofilms》的论文。
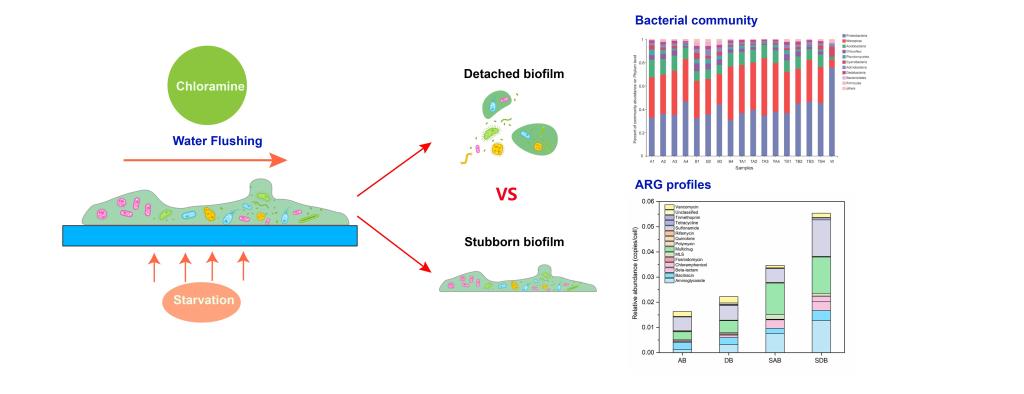
管壁生物膜是供水管网微生物的主要存在场所,而环境条件的变化将导致生物膜脱落进入水中威胁末端用水安全。本研究研究了氯胺消毒剂和饥饿处理对生物膜脱落的影响,结果显示生物膜中细菌的脱落速率随着氯胺浓度的上升而增加,1.0 mg/L 氯胺作用下生物膜中细菌的脱落速率最大。饥饿处理虽然降低了生物膜中的生物量,但是提高了生物膜中细菌的脱落速率。 16S rRNA测序结果表明脱落生物膜与顽固生物膜中的微生物群落组成存在显著差异,顽固生物膜中Nitrospira, Bryobacter, Hyphomicrobium和Pedomicrobium的丰度均显著高于脱落生物膜。氯胺浓度对脱落生物膜的微生物群落的影响不显著,而饥饿处理则会导致生物膜中化能自养型细菌的丰度上升。宏基因组测序结果显示脱落生物膜抗生素抗性基因的丰度显著高于顽固生物膜,而饥饿处理则会提高所有生物膜中的抗性基因丰度。本研究有助于明晰生物膜脱落的风险以及抗性基因在供水系统中的传播规律。
Abstract: Biofilms were one of the main habitats of microbes in the drinking water distribution system. The variation of environmental conditions can lead to the detachment of biofilms and the deterioration of water quality. In this study, the effects of disinfectant exposure and starvation treatment on the detachment of biofilms were investigated. The results showed that detaching rate increased with the concentration of chloramine in the inlet water and 1.0 mg/L of chloramine led to the largest detached biomass. The starvation treatment resulted in less biofilm biomass but the detaching rates of treated biofilms were higher than those without starvation. The 16S rRNA sequencing results showed that detached and stubborn biofilms had a significant difference in microbial diversity and richness. The microbial community composition of the two types of biofilm showed the difference in the abundance of Nitrospira, Bryobacter, Hyphomicrobium, and Pedomicrobium. Chloramine exposure did not have a significant impact on the microbial community while the starvation treatment led to a higher abundance of chemolithotrophs bacteria. Metagenomic results indicated that detached biofilms had higher abundances of ARGs and starvation treatment could enrich the ARGs. The results of this research could provide the knowledge of biofilm sloughing and help understand the health risk of antibiotic resistance in drinking water.
【文章链接】https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S004896972105974X