Li Lianga,b, Weiying Lia,b,c,*, Yue Lia,b, Wei Zhoua,b, Jiping Chena,b
The removal mechanism of sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-nZVI) toward CdII-EDTA.
Abstract
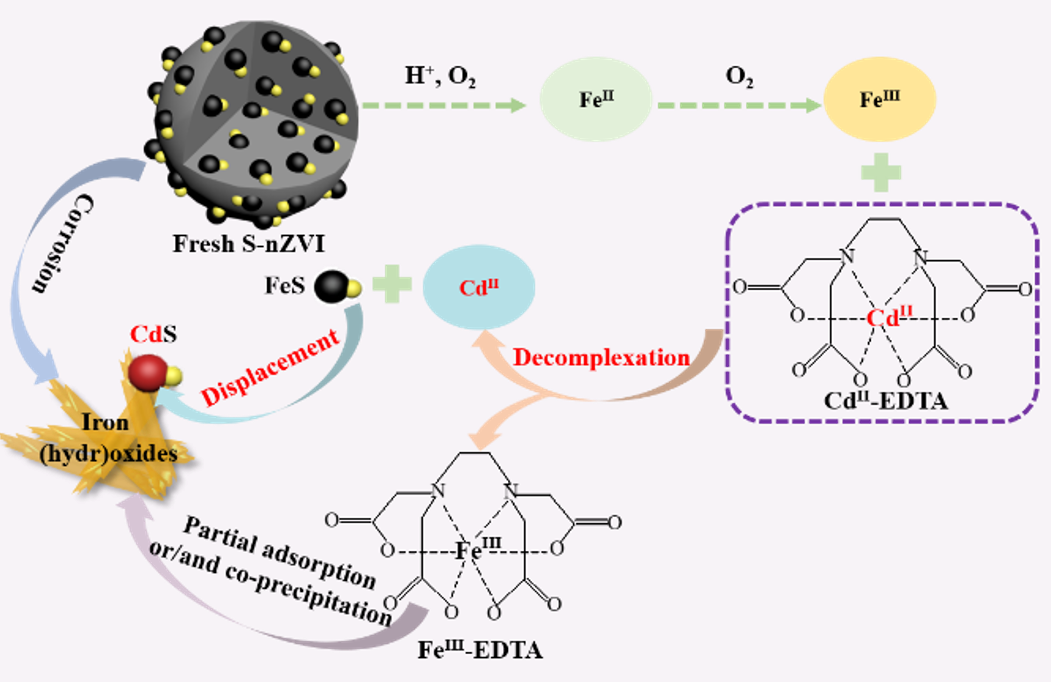
In this study, the removal mechanisms of sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-nZVI) toward EDTA-chelated CdII (CdII-EDTA) and the detailed effects of some critical factors on CdII-EDTA removal by S-nZVI were systematically investigated. The results showed that the removal capacity of S-nZVI toward CdII-EDTA within 90 min of reaction was 746.6 mg/g (when the initial concentration of CdII-EDTA, the dosage of S-nZVI, and the initial solution pH were 300.0 mg CdII/L, 0.3 g/L, and 2.6, respectively), which was 6.2 and 2.5 times higher than that of nZVI and Na2S, respectively, indicating that Fe and S had coupled effect on CdII-EDTA removal. The removal mechanisms of CdII-EDTA by S-nZVI consisted of two-step replacement reactions. In brief, FeIII generated from the corrosion of S-nZVI firstly replaced the CdII in CdII-EDTA, and then the decomplexed CdII ions were immobilized by occurring the second-step replacement reaction with FeS in S-nZVI and forming CdS phase. Batch experiment results indicated that the removal of CdII-EDTA by S-nZVI decreased as the initial CdII-EDTA concentration increased and S-nZVI dosage decreased. Under the same S-nZVI dosage (0.3 g/L) and initial CdII-EDTA concentration (300.0 mg CdII/L), the acidic initial pH (pH0 = 2.6) was favorable for the removal of CdII-EDTA. This study demonstrated that S-nZVI could be a viable choice for the CdII-EDTA-contaminated wastewater treatment.
本研究系统地研究了硫化纳米零价铁(S-nZVI)对EDTA络合态镉(CdII-EDTA)的去除机理以及一些关键因素对S-nZVI去除CdII-EDTA的影响。结果表明,反应90 min,S-nZVI对CdII-EDTA的去除容量为746.6 mg/g(当CdII-EDTA的初始浓度、S-nZVI的投加量、初始pH分别为300.0 mg CdII/L、0.3 g/L和2.6时),分别是nZVI和Na2S对CdII-EDTA去除容量的6.2倍和2.5倍,说明Fe和S对CdII-EDTA的去除具有耦合作用。S-nZVI对CdII-EDTA的去除机理为两步置换反应。简而言之,S-nZVI在腐蚀过程中产生的FeIII首先置换出CdII-EDTA中的CdII离子,然后游离态CdII与S-nZVI中的FeS发生第二步置换反应,形成CdS。批实验结果表明,S-nZVI对CdII-EDTA的去除率随着CdII-EDTA初始浓度的增加而降低,随S-nZVI投加量的增加而增加。在S-nZVI剂量(0.3 g/L)和初始CdII-EDTA浓度(300.0 mg CdII/L)相同的条件下,酸性初始pH (pH0 = 2.6)有利于CdII-EDTA的去除。本研究表明,S-nZVI是处理含CdII-EDTA废水的可行选择。
【全文链接】https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1383586621010418