Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125310
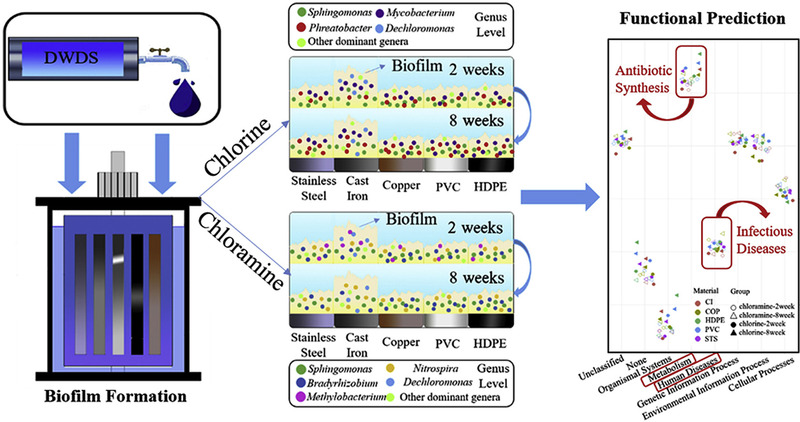
The bacterial composition of biofilms in drinkingwater distribution systems is significantly impacted by the disinfection regimeand substrate material. However, studies that have addressed the changes in thebiofilm community during the early stage of formation (less than 10 weeks) werenot yet adequeate. Here, we explore the effects of the substrate materials(cast iron, stainless steel, copper, PVC, and HDPE) and different disinfectants(chlorine and chloramine) on the community composition and function of young biofilmby using 16S rDNA sequencing. The results showed that Alphaproteobacteria(39.14%-80.87%) and Actinobacteria (5.90%-40.03%) were the dominant classes inchlorine-disinfection samples, while Alphaproteobacteria (17.46%-74.18%) andBetaproteobacteria (3.79%-68.50%) became dominant in a chloraminated group. Theinfrequently discussed genus Phreatobacter became predominant in thechlorinated samples, but it was inhibited by chloramine and copper ions. Thekey driver of the community composition was indicated as differentdisinfectants according to PCoA and Adonis tests, and the bacterial communitychanged significantly over time. Communities of biofilms grown on cast ironshowed a great distance from the other materials according to Bray-Curtisdissimilarity, and they had a unique dominant genus, Dechloromonas. Ametagenomics prediction based on 16S rDNA was used to detect the functionalpathways of antibiotic biosynthesis and beta-lactam resistance, and it revealedthat several pathways were significantly different in terms of theirchlorinated and chloraminated groups.
饮用水管网系统中生物膜细菌群落组成受消毒方式和管壁基质材料的影响较大。然而,针对生物膜群落在形成初期(小于10周)的变化的相关研究尚不多见。在此,我们利用16S rRNA测序技术,探讨了基质材料(铸铁、不锈钢、铜、PVC和HDPE)和不同消毒剂(氯和氯胺)对年轻生物膜群落组成和功能的影响。结果表明,在氯消毒样品中,Alphaproteobacteria(39.14%-80.87%)和Actinobacteria(5.90%-40.03%)是优势菌纲,而Alphaproteobacteria(17.46%-74.18%)和Betaproteobacteria(3.79%-68.50%)为氯胺消毒样品中的优势纲。在氯消毒的样品中,Phreatobacter属成为优势菌,但其被氯胺和铜离子所抑制。PCoA和Adonis测试结果表明,群落组成的关键驱动力为不同的消毒剂,并且细菌群落随着时间的推移也发生了显著变化。依据Bray-Curtis距离计算结果,铸铁上生长的生物膜群落与其他材料的样品差异较大,并在其中发现一个独特的优势属--去氯单胞菌。采用基于16S rDNA的宏基因组学预测方法检测出了样品中存在抗生素生物合成和β-内酰胺耐药性相关功能途径,结果显示,某些KEGG功能途径丰度在两种消毒样品组之间存在显著差异。